🍬day02
一、今日学习目标
1.指令补充
- 指令修饰符
- v-bind 对样式增强的操作
- v-model 应用于其他表单元素
2.computed 计算属性
- 基础语法
- 计算属性 vs 方法
- 计算属性的完整写法
- 成绩案例
3.watch 侦听器
- 基础写法
- 完整写法
4.综合案例 (演示)
- 渲染 / 删除 / 修改数量 / 全选 / 反选 / 统计总价 / 持久化
二、指令修饰符
1.什么是指令修饰符?
所谓指令修饰符就是通过“.”指明一些指令后缀 不同的后缀封装了不同的处理操作 —> 简化代码
2.按键修饰符
- @keyup.enter —>当点击 enter 键的时候才触发
代码演示:
<div id="app">
<h3>@keyup.enter → 监听键盘回车事件</h3>
<input v-model="username" type="text">
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
username: ''
},
methods: {
}
})
</script>
3.v-model 修饰符
- v-model.trim —>去除首位空格
- v-model.number —>转数字
4.事件修饰符
- @事件名.stop —> 阻止冒泡
- @事件名.prevent —>阻止默认行为
- @事件名.stop.prevent —>可以连用 即阻止事件冒泡也阻止默认行为
<style>
.father {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
margin-top: 20px;
}
.son {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: skyblue;
}
</style>
<div id="app">
<h3>v-model修饰符 .trim .number</h3>
姓名:<input v-model="username" type="text"><br>
年纪:<input v-model="age" type="text"><br>
<h3>@事件名.stop → 阻止冒泡</h3>
<div @click="fatherFn" class="father">
<div @click="sonFn" class="son">儿子</div>
</div>
<h3>@事件名.prevent → 阻止默认行为</h3>
<a @click href="http://www.baidu.com">阻止默认行为</a>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
username: '',
age: '',
},
methods: {
fatherFn () {
alert('老父亲被点击了')
},
sonFn (e) {
// e.stopPropagation()
alert('儿子被点击了')
}
}
})
</script>
三、v-bind 对样式控制的增强-操作 class
为了方便开发者进行样式控制, Vue 扩展了 v-bind 的语法,可以针对 class 类名 和 style 行内样式 进行控制 。
1.语法:
<div>:class = "对象/数组">这是一个div</div>
2.对象语法
当 class 动态绑定的是对象时,键就是类名,值就是布尔值,如果值是true,就有这个类,否则没有这个类
<div class="box" :class="{ 类名1: 布尔值, 类名2: 布尔值 }"></div>
适用场景:一个类名,来回切换
3.数组语法
当 class 动态绑定的是数组时 → 数组中所有的类,都会添加到盒子上,本质就是一个 class 列表
<div class="box" :class="[ 类名1, 类名2, 类名3 ]"></div>
使用场景:批量添加或删除类
4.代码练习
<style>
.box {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
border: 3px solid #000;
font-size: 30px;
margin-top: 10px;
}
.pink {
background-color: pink;
}
.big {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
}
</style>
<div id="app">
<!--绑定对象-->
<div class="box">黑马程序员</div>
<!--绑定数组-->
<div class="box">黑马程序员</div>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {}
})
</script>
四、京东秒杀-tab 栏切换导航高亮
1.需求:
当我们点击哪个 tab 页签时,哪个 tab 页签就高亮
2.准备代码:
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
ul {
display: flex;
border-bottom: 2px solid #e01222;
padding: 0 10px;
}
li {
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
line-height: 50px;
list-style: none;
text-align: center;
}
li a {
display: block;
text-decoration: none;
font-weight: bold;
color: #333333;
}
li a.active {
background-color: #e01222;
color: #fff;
}
</style>
<div id="app">
<ul>
<li><a class="active" href="#">京东秒杀</a></li>
<li><a href="#">每日特价</a></li>
<li><a href="#">品类秒杀</a></li>
</ul>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
list: [
{ id: 1, name: '京东秒杀' },
{ id: 2, name: '每日特价' },
{ id: 3, name: '品类秒杀' }
]
}
})
</script>
3.思路:
1.基于数据,动态渲染 tab(v-for)
2.准备一个下标 记录高亮的是哪一个 tab
3.基于下标动态切换 class 的类名
五、v-bind 对有样式控制的增强-操作 style
1.语法
<div class="box" :style="{ CSS属性名1: CSS属性值, CSS属性名2: CSS属性值 }"></div>
2.代码练习
<style>
.box {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: rgb(187, 150, 156);
}
</style>
<div id="app">
<div class="box"></div>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {}
})
</script>
3.进度条案例
<style>
.progress {
height: 25px;
width: 400px;
border-radius: 15px;
background-color: #272425;
border: 3px solid #272425;
box-sizing: border-box;
margin-bottom: 30px;
}
.inner {
width: 50%;
height: 20px;
border-radius: 10px;
text-align: right;
position: relative;
background-color: #409eff;
background-size: 20px 20px;
box-sizing: border-box;
transition: all 1s;
}
.inner span {
position: absolute;
right: -20px;
bottom: -25px;
}
</style>
<div id="app">
<div class="progress">
<div class="inner">
<span>50%</span>
</div>
</div>
<button>设置25%</button>
<button>设置50%</button>
<button>设置75%</button>
<button>设置100%</button>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {}
})
</script>
六、v-model 在其他表单元素的使用
1.讲解内容:
常见的表单元素都可以用 v-model 绑定关联 → 快速 获取 或 设置 表单元素的值
它会根据 控件类型 自动选取 正确的方法 来更新元素
输入框 input:text ——> value
文本域 textarea ——> value
复选框 input:checkbox ——> checked
单选框 input:radio ——> checked
下拉菜单 select ——> value
...
2.代码准备
<style>
textarea {
display: block;
width: 240px;
height: 100px;
margin: 10px 0;
}
</style>
<div id="app">
<h3>小黑学习网</h3>
姓名:
<input type="text" />
<br /><br />
是否单身:
<input type="checkbox" />
<br /><br />
<!--
前置理解:
1. name: 给单选框加上 name 属性 可以分组 → 同一组互相会互斥
2. value: 给单选框加上 value 属性,用于提交给后台的数据
结合 Vue 使用 → v-model
-->
性别:
<input type="radio" />男 <input type="radio" />女 <br /><br />
<!--
前置理解:
1. option 需要设置 value 值,提交给后台
2. select 的 value 值,关联了选中的 option 的 value 值
结合 Vue 使用 → v-model
-->
所在城市:
<select>
<option>北京</option>
<option>上海</option>
<option>成都</option>
<option>南京</option>
</select>
<br /><br />
自我描述:
<textarea></textarea>
<button>立即注册</button>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {}
})
</script>
七、computed 计算属性
1.概念
基于现有的数据,计算出来的新属性。 依赖的数据变化,自动重新计算。
2.语法
- 声明在 computed 配置项中,一个计算属性对应一个函数
- 使用起来和普通属性一样使用
3.注意
- computed 配置项和 data 配置项是同级的
- computed 中的计算属性虽然是函数的写法,但他依然是个属性
- computed 中的计算属性不能和 data 中的属性同名
- 使用 computed 中的计算属性和使用 data 中的属性是一样的用法
- computed 中计算属性内部的this依然指向的是 Vue 实例
4.案例
比如我们可以使用计算属性实现下面这个业务场景

5.代码准备
<style>
table {
border: 1px solid #000;
text-align: center;
width: 240px;
}
th,
td {
border: 1px solid #000;
}
h3 {
position: relative;
}
</style>
<div id="app">
<h3>小黑的礼物清单</h3>
<table>
<tr>
<th>名字</th>
<th>数量</th>
</tr>
<tr v-for="(item, index) in list" :key="item.id">
<td>{{ item.name }}</td>
<td>{{ item.num }}个</td>
</tr>
</table>
<!-- 目标:统计求和,求得礼物总数 -->
<p>礼物总数:? 个</p>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
// 现有的数据
list: [
{ id: 1, name: '篮球', num: 1 },
{ id: 2, name: '玩具', num: 2 },
{ id: 3, name: '铅笔', num: 5 }
]
}
})
</script>
八、computed 计算属性 VS methods 方法
1.computed 计算属性
作用:封装了一段对于数据的处理,求得一个结果
语法:
- 写在 computed 配置项中
- 作为属性,直接使用
- js 中使用计算属性: this.计算属性
- 模板中使用计算属性:双大括号 计算属性 双大括号
2.methods 计算属性
作用:给 Vue 实例提供一个方法,调用以处理业务逻辑。
语法:
- 写在 methods 配置项中
- 作为方法调用
- js 中调用:this.方法名()
- 模板中调用 双大括号 方法名() 双大括号 或者 @事件名="方法名"
3.计算属性的优势
缓存特性(提升性能)
计算属性会对计算出来的结果缓存,再次使用直接读取缓存,
依赖项变化了,会自动重新计算 → 并再次缓存
methods 没有缓存特性
通过代码比较
<style>
table {
border: 1px solid #000;
text-align: center;
width: 300px;
}
th,
td {
border: 1px solid #000;
}
h3 {
position: relative;
}
span {
position: absolute;
left: 145px;
top: -4px;
width: 16px;
height: 16px;
color: white;
font-size: 12px;
text-align: center;
border-radius: 50%;
background-color: #e63f32;
}
</style>
<div id="app">
<h3>小黑的礼物清单🛒<span>?</span></h3>
<table>
<tr>
<th>名字</th>
<th>数量</th>
</tr>
<tr v-for="(item, index) in list" :key="item.id">
<td>{{ item.name }}</td>
<td>{{ item.num }}个</td>
</tr>
</table>
<p>礼物总数:{{ totalCount }} 个</p>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
// 现有的数据
list: [
{ id: 1, name: '篮球', num: 3 },
{ id: 2, name: '玩具', num: 2 },
{ id: 3, name: '铅笔', num: 5 }
]
},
computed: {
totalCount() {
let total = this.list.reduce((sum, item) => sum + item.num, 0)
return total
}
}
})
</script>
4.总结
1.computed有缓存特性,methods没有缓存
2.当一个结果依赖其他多个值时,推荐使用计算属性
3.当处理业务逻辑时,推荐使用 methods 方法,比如事件的处理函数
九、计算属性的完整写法
既然计算属性也是属性,能访问,应该也能修改了?
- 计算属性默认的简写,只能读取访问,不能 "修改"
- 如果要 "修改" → 需要写计算属性的完整写法
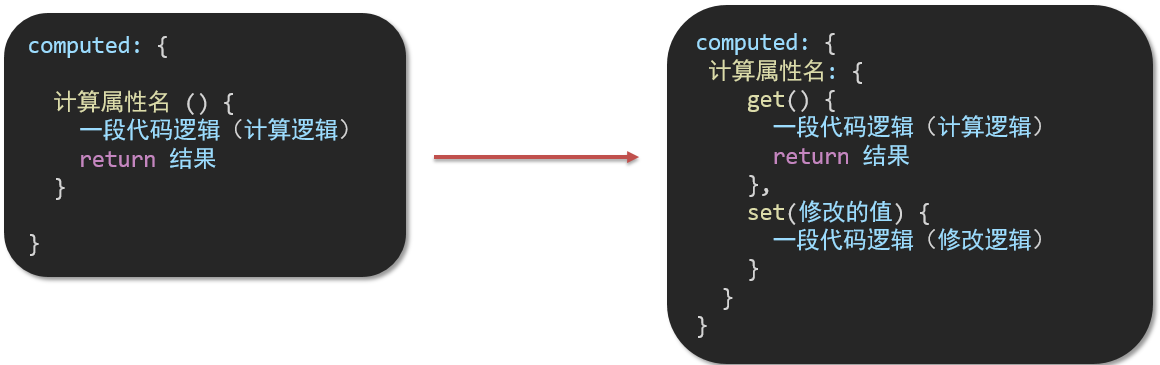
完整写法代码演示
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
姓:
<input type="text" v-model="firstName" />
<br />
名:
<input type="text" v-model="lastName" />
<br />
<p>姓名:{{ fullName }}</p>
<button @click="changeName">修改姓名</button>
</div>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
firstName: '刘',
lastName: '备'
},
computed: {
// // 简写 -> 获取,但没有设置的逻辑
// fullName() {
// return this.firstName + this.lastName;
// },
// 完整写法 -> 获取 + 设置
fullName: {
// 1. 当fullName计算属性: 被获取求值时,执行get(有缓存优先读缓存)
// 会将返回值作为: 求值的结果
get() {
return this.firstName + this.lastName
},
// 2.当fullName计算属性,被修改复制时,执行set
// 修改的字传给set方法的形参
set(value) {
console.log(value)
this.firstName = value.slice(0, 1)
this.lastName = value.slice(1)
}
}
},
methods: {
changeName() {
this.fullName = '吕小布'
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
十、综合案例-成绩案例
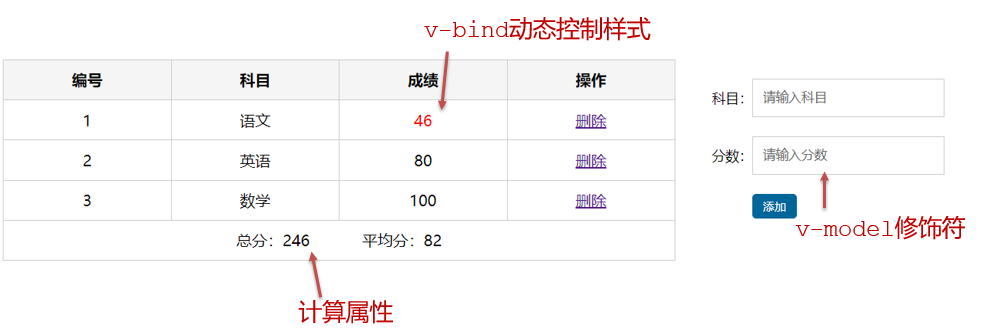
功能描述:
1.渲染功能
2.删除功能
3.添加功能
4.统计总分,求平均分
思路分析:
1.渲染功能 v-for :key v-bind:动态绑定 class 的样式
2.删除功能 v-on 绑定事件, 阻止 a 标签的默认行为
3.v-model 的修饰符 .trim、 .number、 判断数据是否为空后 再添加、添加后清空文本框的数据
4.使用计算属性 computed 计算总分和平均分的值
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./styles/index.css" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app" class="score-case">
<div class="table">
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>编号</th>
<th>科目</th>
<th>成绩</th>
<th>操作</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody v-if="list.length>0">
<tr v-for="(item,index) in list" :key="item.id">
<td>{{ index+1 }}</td>
<td>{{ item.subject }}</td>
<!-- 不及格的标红 条件:分数 < 60-->
<td :class="{red: item.score<60}">{{ item.score }}</td>
<td><a href="https://www.baidu.com" @click.prevent="del(item.id)">删除</a></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
<tbody v-else>
<tr>
<td colspan="5">
<span class="none">暂无数据</span>
</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
<tfoot>
<tr>
<td colspan="5">
<span>总分:{{totalScore}}</span>
<span style="margin-left: 50px">平均分:{{avgScore}}</span>
</td>
</tr>
</tfoot>
</table>
</div>
<div class="form">
<div class="form-item">
<div class="label">科目:</div>
<div class="input">
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入科目" v-model.trim="subject" />
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-item">
<div class="label">分数:</div>
<div class="input">
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入分数" v-model.number="score" />
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-item">
<div class="label"></div>
<div class="input">
<button class="submit" @click="add()">添加</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script src="../vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
list: [
{ id: 1, subject: '语文', score: 20 },
{ id: 7, subject: '数学', score: 99 },
{ id: 12, subject: '英语', score: 70 }
],
subject: '',
score: ''
},
methods: {
del(id) {
console.log(id)
this.list = this.list.filter(item => item.id != id)
},
add() {
if (!this.subject) {
alert('请输入科目')
return
}
if (typeof this.score !== 'number') {
alert('请输入正确的成绩')
return
}
this.list.unshift({
id: +new Date(),
subject: this.subject,
score: this.score
})
this.subject = ''
this.score = ''
}
},
computed: {
totalScore() {
return this.list.reduce((sum, item) => sum + item.score, 0)
},
avgScore() {
if (this.list.length === 0) {
return 0
}
return (this.totalScore / this.list.length).toFixed(2)
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
十一、watch 侦听器(监视器)
1.作用:
监视数据变化,执行一些业务逻辑或异步操作
2.语法:
watch 同样声明在跟 data 同级的配置项中
简单写法: 简单类型数据直接监视
完整写法:添加额外配置项
data: { words: '苹果', obj: { words: '苹果' } }, watch: { // 该方法会在数据变化时,触发执行 数据属性名 (newValue, oldValue) { 一些业务逻辑 或 异步操作。 }, '对象.属性名' (newValue, oldValue) { 一些业务逻辑 或 异步操作。 } }
3.侦听器代码准备
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
font-size: 18px;
}
#app {
padding: 10px 20px;
}
.query {
margin: 10px 0;
}
.box {
display: flex;
}
textarea {
width: 300px;
height: 160px;
font-size: 18px;
border: 1px solid #dedede;
outline: none;
resize: none;
padding: 10px;
}
textarea:hover {
border: 1px solid #1589f5;
}
.transbox {
width: 300px;
height: 160px;
background-color: #f0f0f0;
padding: 10px;
border: none;
}
.tip-box {
width: 300px;
height: 25px;
line-height: 25px;
display: flex;
}
.tip-box span {
flex: 1;
text-align: center;
}
.query span {
font-size: 18px;
}
.input-wrap {
position: relative;
}
.input-wrap span {
position: absolute;
right: 15px;
bottom: 15px;
font-size: 12px;
}
.input-wrap i {
font-size: 20px;
font-style: normal;
}
</style>
<div id="app">
<!-- 条件选择框 -->
<div class="query">
<span>翻译成的语言:</span>
<select>
<option value="italy">意大利</option>
<option value="english">英语</option>
<option value="german">德语</option>
</select>
</div>
<!-- 翻译框 -->
<div class="box">
<div class="input-wrap">
<textarea v-model="words"></textarea>
<span><i>⌨️</i>文档翻译</span>
</div>
<div class="output-wrap">
<div class="transbox">mela</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
<script>
// 接口地址:https://applet-base-api-t.itheima.net/api/translate
// 请求方式:get
// 请求参数:
// (1)words:需要被翻译的文本(必传)
// (2)lang: 需要被翻译成的语言(可选)默认值-意大利
// -----------------------------------------------
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
words: ''
}
// 具体讲解:(1) watch语法 (2) 具体业务实现
})
</script>
十二、翻译案例-代码实现
<script>
// 接口地址:https://applet-base-api-t.itheima.net/api/translate
// 请求方式:get
// 请求参数:
// (1)words:需要被翻译的文本(必传)
// (2)lang: 需要被翻译成的语言(可选)默认值-意大利
// -----------------------------------------------
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
//words: ''
obj: {
words: ''
},
result: '', // 翻译结果
// timer: null // 延时器id
},
// 具体讲解:(1) watch语法 (2) 具体业务实现
watch: {
// 该方法会在数据变化时调用执行
// newValue新值, oldValue老值(一般不用)
// words (newValue) {
// console.log('变化了', newValue)
// }
'obj.words' (newValue) {
// console.log('变化了', newValue)
// 防抖: 延迟执行 → 干啥事先等一等,延迟一会,一段时间内没有再次触发,才执行
clearTimeout(this.timer)
this.timer = setTimeout(async () => {
const res = await axios({
url: 'https://applet-base-api-t.itheima.net/api/translate',
params: {
words: newValue
}
})
this.result = res.data.data
console.log(res.data.data)
}, 300)
}
}
})
</script>
十三、watch 侦听器
1.语法
完整写法 —>添加额外的配置项
- deep:true 对复杂类型进行深度监听
- immdiate:true 初始化 立刻执行一次
data: {
obj: {
words: '苹果',
lang: 'italy'
},
},
watch: {// watch 完整写法
对象: {
deep: true, // 深度监视
immdiate:true,//立即执行handler函数
handler (newValue) {
console.log(newValue)
}
}
}
2.需求
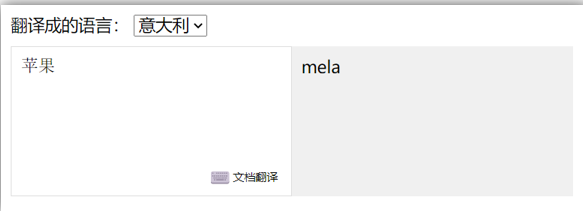
- 当文本框输入的时候 右侧翻译内容要时时变化
- 当下拉框中的语言发生变化的时候 右侧翻译的内容依然要时时变化
- 如果文本框中有默认值的话要立即翻译
3.代码实现
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
obj: {
words: '小黑',
lang: 'italy'
},
result: '', // 翻译结果
},
watch: {
obj: {
deep: true, // 深度监视
immediate: true, // 立刻执行,一进入页面handler就立刻执行一次
handler (newValue) {
clearTimeout(this.timer)
this.timer = setTimeout(async () => {
const res = await axios({
url: 'https://applet-base-api-t.itheima.net/api/translate',
params: newValue
})
this.result = res.data.data
console.log(res.data.data)
}, 300)
}
}
}
})
</script>
4.总结
watch 侦听器的写法有几种?
1.简单写法
watch: {
数据属性名 (newValue, oldValue) {
一些业务逻辑 或 异步操作。
},
'对象.属性名' (newValue, oldValue) {
一些业务逻辑 或 异步操作。
}
}
2.完整写法
watch: {// watch 完整写法
数据属性名: {
deep: true, // 深度监视(针对复杂类型)
immediate: true, // 是否立刻执行一次handler
handler (newValue) {
console.log(newValue)
}
}
}
十四、综合案例
购物车案例
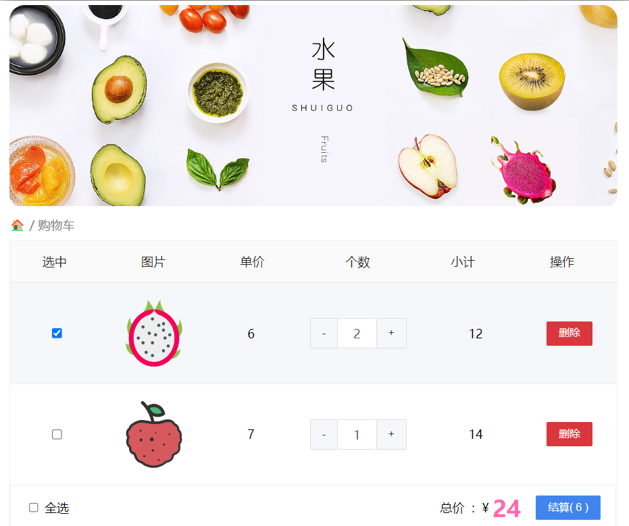
需求说明:
- 渲染功能
- 删除功能
- 修改个数
- 全选反选
- 统计 选中的 总价 和 总数量
- 持久化到本地
实现思路:
1.基本渲染: v-for 遍历、:class 动态绑定样式
2.删除功能 : v-on 绑定事件,获取当前行的 id
3.修改个数 : v-on 绑定事件,获取当前行的 id,进行筛选出对应的项然后增加或减少
4.全选反选
- 必须所有的小选框都选中,全选按钮才选中 → every
- 如果全选按钮选中,则所有小选框都选中
- 如果全选取消,则所有小选框都取消选中
声明计算属性,判断数组中的每一个 checked 属性的值,看是否需要全部选
5.统计 选中的 总价 和 总数量 :通过计算属性来计算选中的总价和总数量
6.持久化到本地: 在数据变化时都要更新下本地存储 watch
代码:(css 代码自己找)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./css/inputnumber.css" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./css/index.css" />
<title>购物车</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="app-container" id="app">
<!-- 顶部banner -->
<div class="banner-box"><img src="http://autumnfish.cn/static/fruit.jpg" alt="" /></div>
<!-- 面包屑 -->
<div class="breadcrumb">
<span>🏠</span>
/
<span>购物车</span>
</div>
<!-- 购物车主体 -->
<div class="main" v-if="fruitList.length > 0">
<div class="table">
<!-- 头部 -->
<div class="thead">
<div class="tr">
<div class="th">选中</div>
<div class="th th-pic">图片</div>
<div class="th">单价</div>
<div class="th num-th">个数</div>
<div class="th">小计</div>
<div class="th">操作</div>
</div>
</div>
<!-- 身体 -->
<div class="tbody">
<div v-for="(item,index) in fruitList" :key="item.id" :class="{tr:true, active:item.isChecked}">
<div class="td"><input type="checkbox" v-model="item.isChecked" /></div>
<div class="td">
<img :src="item.icon" alt="" />
</div>
<div class="td">{{ item.price }}</div>
<div class="td">
<div class="my-input-number">
<button :disabled="item.num <= 1" class="decrease" @click="sub(item.id)">-</button>
<span class="my-input__inner">{{ item.num }}</span>
<button class="increase" @click="add(item.id)">+</button>
</div>
</div>
<div class="td">{{ item.num * item.price }}</div>
<div class="td"><button @click="del(item.id)">删除</button></div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<!-- 底部 -->
<div class="bottom">
<!-- 全选 -->
<label class="check-all">
<input type="checkbox" v-model="isAll" />
全选
</label>
<div class="right-box">
<!-- 所有商品总价 -->
<span class="price-box">
总价 : ¥
<span class="price">{{totalPrice}}</span>
</span>
<!-- 结算按钮 -->
<button class="pay">结算( {{totalCount}} )</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<!-- 空车 -->
<div class="empty" v-else="">🛒空空如也</div>
</div>
<script src="../vue.js"></script>
<script>
const defaultArr = [
{
id: 1,
icon: 'http://autumnfish.cn/static/火龙果.png',
isChecked: true,
num: 2,
price: 6
},
{
id: 2,
icon: 'http://autumnfish.cn/static/荔枝.png',
isChecked: false,
num: 7,
price: 20
},
{
id: 3,
icon: 'http://autumnfish.cn/static/榴莲.png',
isChecked: false,
num: 3,
price: 40
},
{
id: 4,
icon: 'http://autumnfish.cn/static/鸭梨.png',
isChecked: true,
num: 10,
price: 3
},
{
id: 5,
icon: 'http://autumnfish.cn/static/樱桃.png',
isChecked: false,
num: 20,
price: 34
}
]
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
// 水果列表
fruitList: JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem('list')) || defaultArr
},
computed: {
// isAll() {
// // 必须所有的小选框 都选中,全选按钮才选中 every
// return this.fruitList.every(item => item.isChecked);
// },
isAll: {
get() {
return this.fruitList.every(item => item.isChecked)
},
set(val) {
// 基于拿到的Boolean值 要让所有的小选框,同步状态
this.fruitList.forEach(item => {
item.isChecked = val
})
}
},
// 统计选中的总数
totalCount() {
return this.fruitList.reduce((sum, item) => (item.isChecked ? sum + item.num : sum), 0)
},
// 统计选中的价格
totalPrice() {
return this.fruitList.reduce((sum, item) => (item.isChecked ? sum + item.num * item.price : sum), 0)
}
},
methods: {
del(id) {
this.fruitList = this.fruitList.filter(item => item.id != id)
},
add(id) {
// 根据ID找到数组中 对应项
const fruit = this.fruitList.find(item => item.id === id)
fruit.num++
// console.log(fruit);
},
sub(id) {
const fruit = this.fruitList.find(item => item.id === id)
fruit.num--
// console.log(fruit);
}
},
watch: {
fruitList: {
deep: true,
handler(newValue) {
// 需要将变化后的newValue 存入本地 (转JSON)
localStorage.setItem('list', JSON.stringify(newValue))
console.log(newValue)
}
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>